Screening Assistant 2
Workers
Last edited: 06/07/2011
By: VLG
Sourceforge: SA2 website
Help: SA2 forums
Documentation index
This page introduces the default Workers currently available in SA2. Workers are basically additional sets of operations that can optionally be performed on each molecule: when importing a new set of compounds, the selected worker(s) will perform additional operations on each non-duplicate molecule. Note that by default, each worker do not necessarily compute all its available operations. Check the detailed documentation of each worker to know more about this.
Table of Contents
JOELib worker - top
The JOELib worker allows you to compute one fingerprint and various other descriptors which were available in the first version of Screening Assistant. By default, the worker will only compute the fingerprint.
SSKey-3DS fingerprint
This fingerprint encodes both simple properties as well as various substructures. It is based on the JOELib library, and was already available in the first version of SA. The following figure explains in more detail the information contained in the fingerprint.
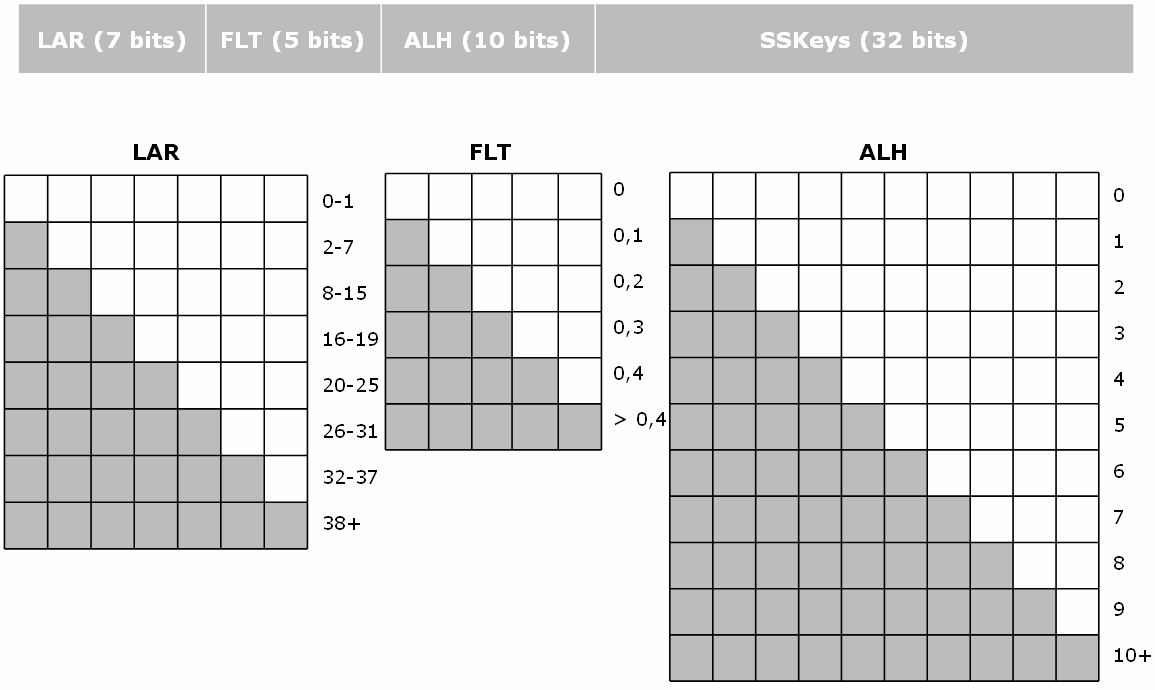
The ALH part corresponds to the number of hydrogen bond acceptors, the LAR part to the number of aromatic bonds, and the FLT part corresponds to the proportion of rotatable bonds found in the molecule. All these properties are encoded in a binary form. The remaining of the fingerprint encodes the presence / absence of various substructures.
Descriptors
The descriptors are the same as computed in the first version of SA1. They include simple physico-chemical and constitutional descriptors, as well as various other flags and in-house descriptors such as the Progressive Drug-like and Progressive Lead-like descriptors.
Note that the Reactive and Warhead flags will contain the same value as those stored in the Basic descriptors table if you use the JOELib handler for your database (which is currently the default handler).
Default parameters - top
The worker will perform the following calculations by default (untill you change it)
- SSKey-3DS fingerprint
CDK worker - top
Two workers are available for the CDK library. One makes it possible to compute various fingerprints, with the other allows one to compute descriptors. Dedicated tables have been created in the database to store these information, as detailed in the Properties section.
Descriptors - top
Almost all descriptors available in the CDK can be computed. Almost... There is actually a bunch of descriptors that, although available in the database, will never be computed because they are (i) too slow to calculate, or (2) known to be incorrect. Here is the full list of these descriptors:
- FMF descriptors - Descritor that characterizes molecular complexity and which have been found to be very slow on moderately-sized molecules.
- WHIM descriptors - Descriptors that are known to be incorrect.
- Ionisation Potential - Too slow.
What if you still want to have these descriptors in the database ? Well, you will have to get your hands dirty and do some JAVA programming to perform the calculation yourself. Or just wait for improvements in the CDK library.
Fingerprints - top
Several fingerprints are available in the CDK library, and some of them can be computed and / or stored using the CDK worker.
- MACCS (166 bits)
The MACCS fingerprint as defined in the CDK (the SMART patterns have been taken from the RDKit according to the documentation, and bits 1 and 44 are completely ignored because of missing specifications). - E-State (79 bits)
A fingerprint that encode the presence / absence of EState fragments. According to the CDK documentation, the SMART patterns have been taken from the RDKit library. - Pubchem (881 bits)
A structural substructure fingerprint. A detailed description of this fingerprint can be found here. The CDK implementation uses a slightly modified version. - Hybridization (1024 bits)
A fingerprint that takes into account SP2 hybridization instead of aromaticity. A Search Depth of 6 is used here.
Default parameters - top
The worker will perform the following calculations by default (untill you change it)
- Consitutional descriptors
- Electronic descriptors
- Hybrid descriptors
- Topological descriptors
- Protein descriptors
- MACCS fingerprint